Strengthening India’s Agricultural Backbone
Key Achievements and Government Initiatives
Synopsis
- The Government of India has significantly increased budget allocations, rising from ₹11,915.22 crore in 2008-09 to ₹1,22,528.77 crore in 2024-25, demonstrating its commitment to the sector.
- Food grain production has surged from 204.6 million tonnes (2004-05) to an estimated 332.3 million tonnes (2023-24), with enhanced productivity and Minimum Support Price (MSP) revisions ensuring better farmer incomes.
- The MSP for paddy and wheat has grown from ₹850 and ₹1,080 per quintal in 2008-09 to ₹2,300 and ₹2,425 per quintal in 2023-24 respectively. Additionally, the total MSP paid to farmers for paddy and wheat has surged from ₹4.40 lakh crore and ₹2.27 lakh crore in 2004-13 to ₹12.51 lakh crore and ₹5.44 lakh crore in 2014-24 respectively.
- Key farmer-centric initiatives include PM-KISAN (₹3.46 lakh crore disbursed), PMFBY (₹1.65 lakh crore in claims), and e-NAM, which has integrated 1,400+ mandis for better market access. The Agricultural Infrastructure Fund (AIF) has sanctioned ₹52,738 crore for over 87,500 projects to improve post-harvest management.
- The government’s millet promotion efforts have boosted production, while institutional credit expansion, Kisan Credit Card (KCC) growth, and agricultural R&D investments continue to transform the sector.
Agriculture serves as the backbone of India’s economy, playing a pivotal role in ensuring food security, providing employment, and contributing to overall economic development. It supports the livelihoods of a significant portion of the population and remains vital to India’s socio-economic fabric. Recognizing its importance, the Government of India has implemented various initiatives and significantly increased budget allocations to strengthen the sector.
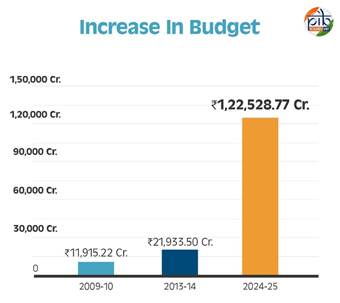
Enhanced Budget Allocation
The budget estimates for the Department of Agriculture, Cooperation & Farmers Welfare was ₹11,915.22 Crore in 2008-09. The budget forDepartment of Agriculture and Farmers’ Welfare increased to ₹21,933.50 Crore in 2013-14 and further advanced to ₹1,22,528.77 Crore in 2024-25, reflecting the government’s commitment to agricultural development.
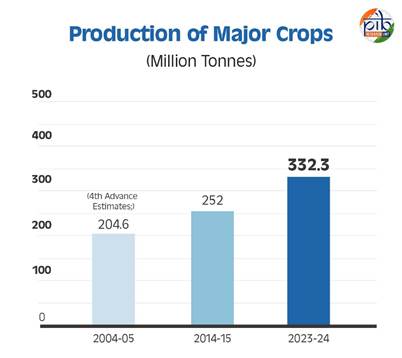
Increased Food Grain Production
India’s foodgrain production has seen a steady rise over the years, reflecting improvements in agricultural productivity and policy support. In 2004-05, total foodgrain production stood at 204.6 million tonnes. (4th advance estimates) This increased to 252 million tonnes in 2014-15 and further surged to an estimated 332.3 million tonnes in 2023-24.
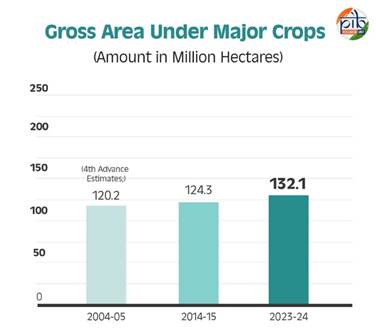
Gross Area Under Major Crops
In 2004-05, the total area under foodgrain crops was 120.2 million hectares ( 4th advance estimates). This expanded to 124.3 million hectares in 2014-15 and reached 132.1 hectares in 2023-24
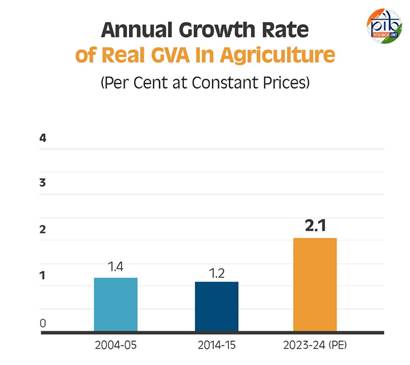
Annual Growth Rate of Real Gross Value Added (GVA) at Basic Prices
The annual growth rate of real GVA in the agriculture, forestry, and fishing sector has shown fluctuations over the years. In 2004-05, it was recorded at 1.4%, slightly declining to 1.2% in 2014-15. However, the sector has gained momentum in recent years, with the growth rate rising to an estimated 2.1% in 2023-24. This reflects improved efficiency, mechanization, and diversification in agricultural activities.
Real Gross Value Added (GVA) in Agriculture (₹ Crore at Constant Prices)
The real GVA for agriculture, forestry, and fishing has demonstrated substantial growth, showcasing the sector’s increasing contribution to the economy. In 2004-05, the GVA stood at ₹13.85 lakh crore, which rose to ₹18.94 lakh crore in 2014-15 and further increased to an estimated ₹26.42 lakh crore in 2023-24( PE). This consistent rise highlights the sector’s resilience and its vital role in India’s economic development.
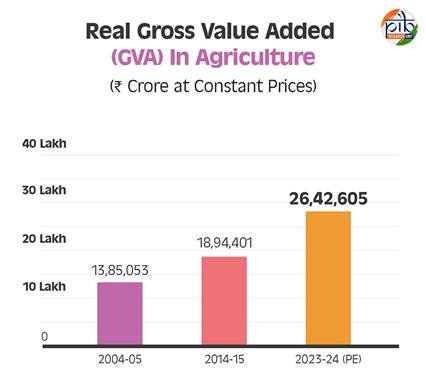
Increase in productivity
Comparison of yield between 2013-14 and 2023-24 (Kg/ha) reflects a substantial increase in productivity.
| Crop | 2013-14 | 2023-24 | Absolute Difference (2023-24 over 2013-14) | Difference(%) |
| Rice | 2416 | 2882 | 466 | 19.29 |
| Wheat | 3145 | 3559 | 414 | 13.16 |
| Maize | 2676 | 3351 | 675 | 25.22 |
| Coarse Cereals | 1717 | 2945 | 1228 | 71.52 |
| Total Pulses | 763 | 881 | 118 | 15.47 |
| Total Foodgrains | 2120 | 2515 | 395 | 18.63 |
| Total Oilseeds | 1167 | 1314 | 147 | 12.60 |
| Sugarcane | 70522 | 78953 | 8431 | 11.96 |
| Jute | 2639 | 2783 | 144 | 5.46 |
Food Grain Procurement
- The decade from 2014-15 to 2023-24 witnessed an impressive 6900 LMT of paddy procurement, a substantial increase from the 4590 LMT procured in the preceding ten years (2004-05 to 2013-14).
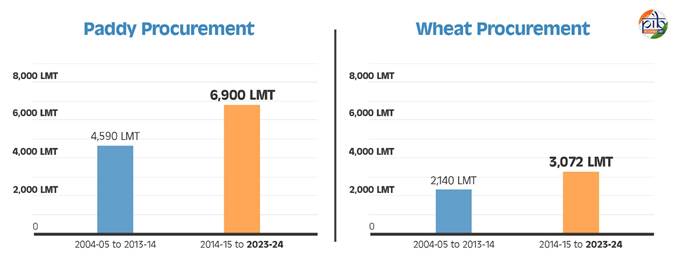
- Similarly, wheat procurement has seen a substantial surge, thanks to proactive planning and meticulous execution. The procurement increased from 2140 LMT in 2004-05 to 2013-14 to 3072 LMT in 2014-23.
Minimum Support Price (MSP) Enhancements
- Government has increased the MSP for all mandated Kharif, Rabi and other commercial crops with a return of at least 50 per cent over all India weighted average cost of production from 2018-19.
- The MSP for paddy (common) has risen from ₹850 per quintal in 2008-09 (with an additional incentive of ₹50 per quintal) to ₹1,310 per quintal in 2013-14, and further to ₹2,300 per quintal in 2023-24.
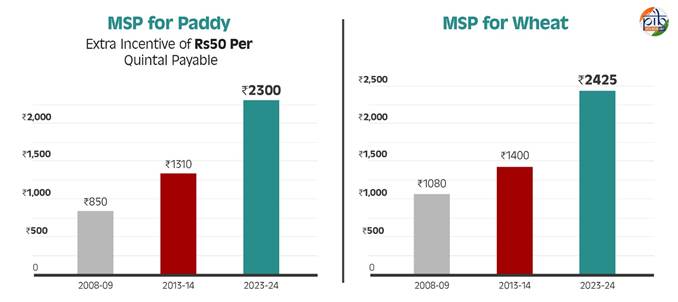
- MSP for wheat has also seen consistent growth, rising from ₹1,080 per quintal in 2008-09 to ₹1,400 per quintal in 2013-14, and reaching ₹2,425 per quintal in 2023-24.
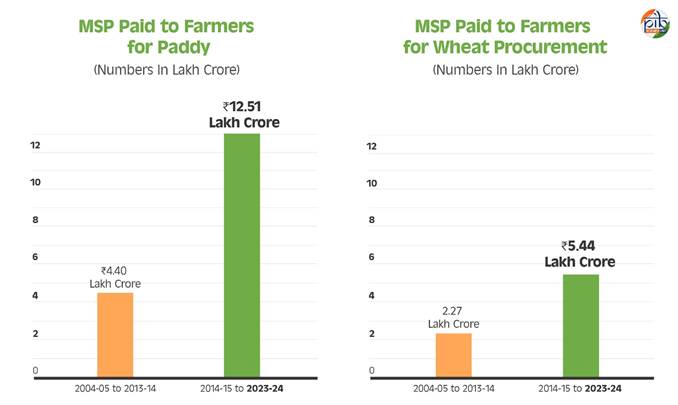
- The MSP paid to farmers for paddy also saw a threefold increase, from ₹4.40 lakh crore in 2004-13 to a staggering ₹12.51 lakh crore in 2014-24.
- The MSP paid to farmers for wheat procurement also saw a steep rise from ₹2.27 lakh crore in 2004-13 to ₹5.44 lakh crore in 2014-24, ensuring greater financial stability for wheat farmers across the country
Income Support through PM-KISAN
Launch of PM-KISAN in 2019 an income support scheme providing ₹ 6000 per year in 3 equal instalments. So far, more than ₹ 3.46 lakh Crore has been disbursed to over 11 Crore farmers through 18 instalments.
Pradhan Mantri Kisan Maandhan Yojana
PMKMY is a central sector scheme, is a voluntary and contributory pension scheme for the entry age group of 18 to 40 years with a provision of ₹ 3000/- monthly pension on attaining the age of 60 years, subject to exclusion criteria. Since the inception of the scheme, over 24.67 lacs small and marginal farmers have joined the PMKMY scheme.
Pradhan Mantri Fasal Bima Yojana (PMFBY)
- was launched in 2016 addressing problems of high premium rates for farmers and reduction in sum insured due to capping. In past 8 Years of implementation. In past 8 Years of implementation, 63.11 Crore farmer applications have been enrolled and over 18.52 Crore (Provisional) farmer applicants have received claims of over ₹ 1,65,149 Crore. During this period nearly ₹ 32,482 Crore were paid by farmers as their share of premium against which claims over ₹ 1,65,149 Crore (Provisional) have been paid to them. Thus, for every ₹100 of premium paid by farmers, they have received about ₹ 508 as claims.
Institutional credit for agriculture sector
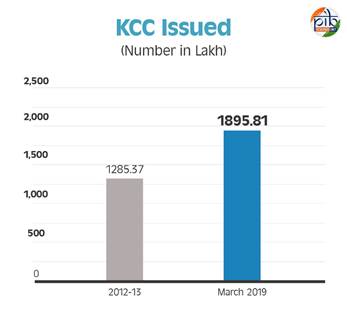
- Since the inception of the scheme, a total of 1,285.37 lakh KCCs had been issued till 2012-13, which increased to 1,895.81 lakh by March 31, 2019 (PE).
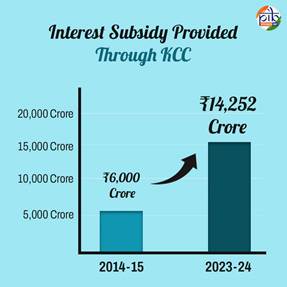
- In the last 10 years, Rs 1.44 lakh Crore of Interest Subsidy has been released on Kisan Credit Card loans. It has risen nearly 2.4 times, from ₹6,000 Crore in 2014-15 to ₹14,252 crore in 2023-24.
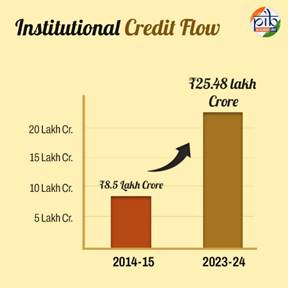
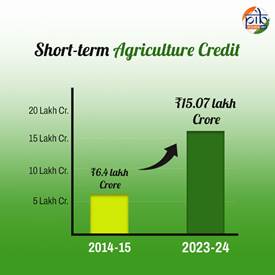
- Institutional credit flow to agriculture has risen nearly three times since 2014-15, rising from ₹ 8.5 lakh Crore to ₹ 25.48 lakh Crore in 2023-24. Short-term agriculture credit has more than doubled, increasing from ₹ 6.4 lakh Crore in 2014-15 to ₹ 15.07 lakh Crore in 2023-24.
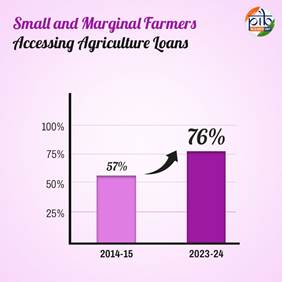
- The proportion of Small and Marginal Farmers accessing agriculture loans grew from 57% in 2014-15 to 76% in 2023-24.
e-NAM
The Department has integrated 1410 mandis with e-NAM since inception across 23 States & 4 UTs. As on 31st December 2024, 1.79 Crore farmers & 2.63 lakh traders have been registered on e-NAM portal. Total volume of 11.02 Crore MT & 42.89 Crore numbers (bamboo, betel leaves, coconut, lemon & sweet corn) collectively worth approximately Rs. 4.01 lakh Crore of trade has been recorded on e-NAM platform.
Agricultural Infrastructure Fund
A One Lakh Crore, Agriculture Infrastructure Fund (AIF) scheme was launched with an objective to mobilize a medium – long term debt financing facility for investment in viable projects for post-harvest management infrastructure and community farming assets through incentives and financial support in order to improve agriculture infrastructure in the country. As on 27.12.2024, ₹ 52,738 Crore have been sanctioned for 87,548 projects under AIF, out of this total sanctioned amount 39,959 Crore are covered under scheme benefits. These sanctioned projects have mobilized an investment of ₹ 86,798 Crore in agriculture sector.
Millets: Superfood of India
During the budget Announcement 2023-24, a “Global R&D Hub for millets in India” was announced with a total budget outlay of ₹ 250 Crore during 2023-24 to 2025-26. for making India a Global R&D Hub.
Key Achievements
- Millet production has increased in the last 1 year, reaching 175.72 lakh tonnes in 2023-24 (Final Estimate) from 173.21 lakh tonnes in 2022-23.
- Productivity has increased by 7% from 1248 Kg/ha to 1337 Kg/ha between 2019 and 2024 (Final Estimate).
- 25 seed hubs have been established in collaboration with ICAR, ensuring the availability of high-quality seeds of improved millet varieties.
- Procurement of 7.8 lakh tonnes of millets during the kharif marketing season of 2023-24
These efforts have led to substantial improvements in food grain production, increased income for farmers, enhanced credit facilities, and better crop insurance. As a result, the agriculture sector continues to evolve and thrive, securing India’s position as a global leader in agricultural production and export.
References
Department of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare
*******
Santosh Kumar/ Sarla Meena/ Madiha Iqbal
(Release ID :266811)



















